Magnesium deficiency
Magnesium, an essential mineral in our organism and involved in most of the major metabolic and biochemical processes in our body. Magnesium needs vary from one individual to another and are increased in certain physiological situations. The lack of magnesium can have multiple repercussions on our health.
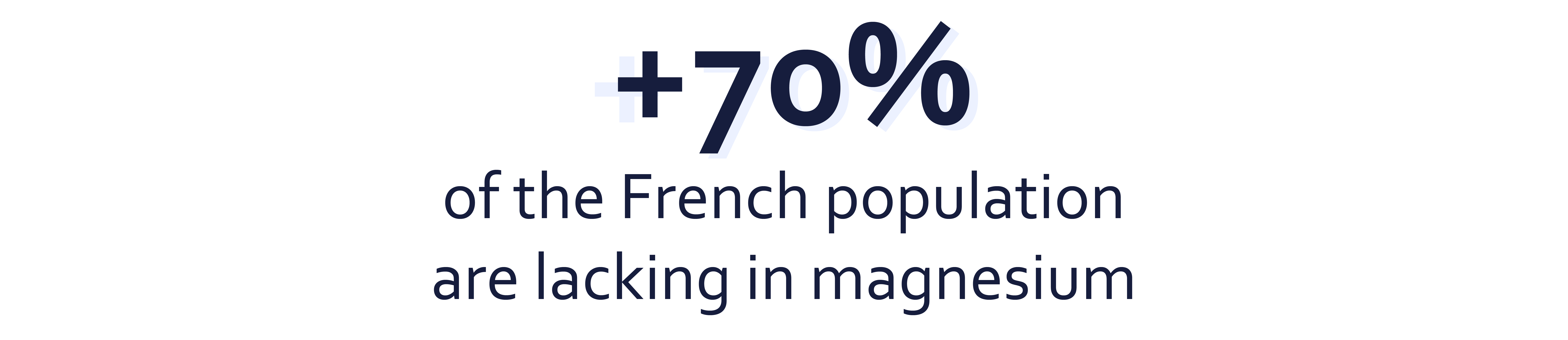

What is the role of magnesium in the body?
Magnesium plays a fundamental role in the correct functioning of the body.
It is present in a large number of metabolic processes and takes part in more than 300 enzymatic reactions(1) such as energy metabolism, protein and DNA synthesis, muscle and nerve function, maintenance of bone structure, blood sugar levels and blood pressure control.
Where is magnesium found in the body(1) ?
Magnesium is one of the most abundant minerals in our body.
It is estimated that a healthy adult body contains an average of 25 g of magnesium. Most of the magnesium is stored in the bones (50 to 60%). The rest is located in muscles (20%) and soft tissue (heart, liver, kidneys, bronchus…). Extracellular magnesium represents only 1% of bodily magnesium.
What are the magnesium requirements of adults and children(2) ?
The French Agency for Food, Environmental and Occupational Health & Safety (ANSES) has defined satisfactory intakes (AI) of magnesium according to age, sex and physiological condition.
- Magnesium intake for men is 380 mg/d and for women 300 mg/d
- For children, the satisfactory intake depends on age
In certain situations, magnesium needs are increased, in particular during pregnancy, breastfeeding or growth periods.
What are the symptoms of a magnesium deficiency?
Magnesium is involved in more than 300 enzymatic reactions(1) in the organism. If the dietary intake of magnesium is insufficient, many important physiological functions can be disrupted leading to the appearance of various symptoms such as:
Abnormal fatigue
Nervousness, irritability, anxiety
Vertigo, nausea, dizziness, headaches
Cramps, muscle contractures, tingling sensations
Twitching of the eyelids
Sleep disorders
Cardiovascular disorders:
high blood pressure, tachycardia
Impaired attention span
What are the causes of magnesium deficiency?
According to a study(3) recording the consumption of the French population, 72% of men and 77% of women have magnesium intakes below the recommended nutritional intake. According to the same study, 18% of men and 23% of women receive less than 2/3 of the recommended nutritional intake.
The lack of magnesium in the organism can have various origins such as:

Insufficient dietary intake or
an unbalanced diet

Chronic stress

Significant sports activity
Certain intestinal or renal diseases

Certain medications:
diuretics, birth control pills, etc..

Chronic alcohol consumption
Which foods are the richest in magnesium?
Magnesium is an “essential” mineral. It is essential to the proper functioning of the body, but the body does not produce it naturally. It is therefore essential to provide a constant and sufficient supply of magnesium every day through the diet.
Favouring certain foods is a good way to have a natural supply of magnesium. Foods rich in magnesium:
Oleaginous fruit and
dried vegetables
Whole grains
Seafood and
oily fish
Green vegetables
Cocoa and dark chocolate
Conversely, it is recommended to limit the consumption of refined cereals and ultra-processed products because their magnesium content is very low.
(1)https://www.revmed.ch/revue-medicale-suisse/2016/revue-medicale-suisse-535/le-magnesium-dans-la-pratique-clinique-quotidienne (consulté le 30/05/2022)
(2) https://www.anses.fr/fr/content/les-r%C3%A9f%C3%A9rences-nutritionnelles-en-vitamines-et-min%C3%A9raux (consulté le 30/05/2022)
(3) Dietary magnesium intake in a French adult population, P. Galan and al, étude SU.VI.MAX. Décembre 1997.

